The short-term outlook for growth in the euro area has deteriorated, while over the medium term the economy should gradually return to moderate growth as both domestic and foreign demand recover.
Euro area economic activity grew at a subdued paced in the first half of 2023, despite the elevated level of manufacturing order backlogs and the unwinding of high energy prices.
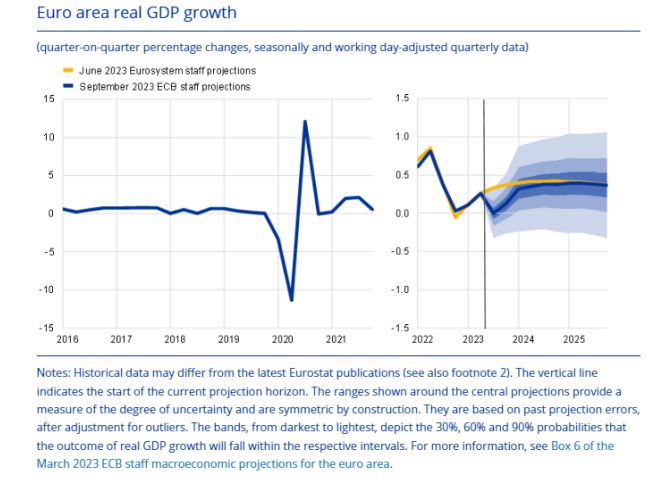
GDP growth
GDP growth is projected to stagnate in the third quarter of 2023 and remain subdued in the fourth quarter as activity in the manufacturing sector remains weak and that in the services sector is expected to slow down.
Over the medium term, euro area GDP growth is projected to moderately strengthen as household real incomes rise and foreign demand improves, albeit with headwinds from tighter financing conditions and declining fiscal support.
Compared with the June 2023 projections, real GDP growth has been revised down by 0.2 percentage points for 2023, 0.5 percentage points for 2024 and 0.1 percentage points for 2025.
• household real consumption is expected to gradually recover and underpin economic growth as uncertainty declines and real incomes and confidence improve.
• real disposable income is projected to recover in 2023 and support consumption, reflecting falling inflation and robust wage growth.
• the household saving ratio is expected to remain elevated in 2023, normalising only gradually thereafter.
Assumptions related to interest rates, commodity prices and exchange rates
Compared with the June 2023 projections, the technical assumptions include higher interest rates as well as higher oil and natural gas prices, lower wholesale electricity prices and an appreciation of the euro.
• The technical assumptions for oil prices have been revised up by over 10% on average over the projection horizon, as concerns about insufficient oil supply outweighed worries over global oil demand.
• The gas price assumptions have increased to a lesser extent than those for oil prices, and electricity price assumptions have decreased.
• Bilateral exchange rates are assumed to remain unchanged over the projection horizon, at the average levels prevailing in the ten working days ending on the cut-off date.
Housing investment is expected to contract over the projection horizon in reaction to tighter financing costs and credit standards.
Business investment is expected to decline in 2024 as tighter financing conditions take a heavy toll;
improving domestic and global demand and the green and digital transition are seen to be the drivers of a mild recovery thereafter.
International environment
Global economic activity moderated in the second quarter of 2023 after strong growth in the first quarter.
Despite relatively resilient global economic activity, global trade is expected to stagnate this year, returning to its historical relationship with real GDP later in the projection horizon and also leading to an improvement in euro area foreign demand.
Inflation, CPI, HICP
Global headline inflation is receding but underlying inflationary pressures remain strong, particularly among advanced economies, whereas export prices of euro area competitors are projected to decline sharply, driven by commodity price developments.
World headline consumer price index inflation is projected to reach 4.8% this year and to decline gradually to 4.2% and 3.2% in 2024 and 2025 respectively. Global inflation projections for this year are broadly unchanged compared with the June projections, but slightly higher for 2024. This largely reflects upward revisions to Türkiye’s inflation outlook and more persistent inflation in the United Kingdom following several upside surprises in data on consumer price inflation and wages.
HICP inflation is projected to decrease from an average of 8.4% in 2022 to an average of 5.6% in 2023, 3.2% in 2024 and 2.1% in 2025
Scenario analysis – Economic slowdown in China
The scenario would imply weaker growth and inflation in the euro area. In the scenario, euro area real GDP growth would decrease by 0.2 percentage points in both 2024 and 2025 compared with the September 2023 baseline, initially owing mostly to lower world (euro area foreign) demand, while the impact via financial channels would be responsible for the bulk of the effect in 2025. The impact on oil prices would give rise to a decrease in euro area inflation of 0.1 percentage points in 2024. The contribution of lower energy prices to
euro area inflation would gradually dissipate by the end of the projection horizon as the demand-supply balance in the commodity market is re-established, while trade and financial spillovers would become more important and lead to a further 0.1 percentage point decrease in 2025.
The fiscal stance is projected to be neutral in 2023 and 2025 but to tighten in 2024; compared with the June projections, fiscal assumptions imply some more discretionary tightening at the euro area level, particularly in 2023.
The euro area fiscal outlook is set to improve over the projection horizon, but less than foreseen in the June 2023 projections. The budget deficit is projected to continue to decline in 2023 and 2024, falling to 2.8% of GDP, but to increase slightly again to 2.9% of GDP in 2025.

COMMENTS